You won't want to miss our China visa guide if you're planning to travel to China! This article explains all you need to know about China visas, from the country's visa-free policy to the detailed application procedure.
China’s Visa Free Policy for Singaporeans
Fortunately, Singapore and China have agreed to a 30-day mutual visa-free entrance beginning on February 9, 2024, which means you can enjoy 30 days of visa-free travel to China.
This is a convenient and welcome change for Singaporeans who are planning short-term travels to China for business, tourism, sightseeing, visiting friends and family, or other private matters. Although China entry requirements for Singaporeans are easier now, a China visa is still necessary if you intend to remain for more than 30 days or if you have a certain kind of visit in mind.
👀Tip: Always ensure your passport is valid for at least six months from your date of entry and check for any updates or travel advisories before your trip.
Visa Tips for Staying in China Over 30 Days

Does Singaporean need Visa to China if planning to stay longer than 30 days?
The answer is yes. While Singaporeans can now enjoy 30-day visa-free entry into China, if your visit exceeds this period, you will need to apply for the appropriate visa.
Specific purposes beyond tourism
If you're visiting for purposes other than short-term tourism, you will also need to apply for China Visa, such as:
- Business (M Visa)
- Work (Z Visa)
- Study (X Visa)
- Journalism (J Visa)
- Family reunions exceeding 30 days (S or Q Visa)
China Visa Free Countries

In order to boost inbound tourism and facilitate easier international exchanges, China is visa-free to some countries and regions.
Which countries can travel to China without visa? Here is the summary.
Region | Countries & Regions | Visa-Free Stay Duration |
Asia | Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, South Korea, Brunei, Japan, UAE, Qatar, Maldives, Kazakhstan, Armenia, Georgia | Up to 15 or 30 days |
Europe | France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Ireland, Norway, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Belgium, Luxembourg, Austria, Greece, Hungary, Czechia, Slovakia, Poland, Portugal, Malta, Estonia, Latvia, Croatia, Romania, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Albania, Belarus, Bosnia & Herzegovina, San Marino, Monaco, Liechtenstein, Iceland | Up to 15 or 30 days |
Oceania | Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, Tonga, Solomon Islands | Up to 30 days |
Americas | Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Ecuador, Grenada, Suriname, Antigua & Barbuda | Up to 30 days |
Africa | Seychelles, Mauritius | Up to 30 days |
👉Note: The maximum stay is typically 15 or 30 days, depending on bilateral agreements or China’s specific policy. The expanded visa-free policy is typically valid until 31 December, 2025. For the latest updates, you can visit the China Visa Appilication Center or China National Immigration Administration website.
China Visa Types

Here's a table summarising the main types of China visas for Singaporeans and international travellers:
Visa Type | Purpose | Duration |
L Visa | Leisure, sightseeing, visiting friends/family | 30 to 90 days |
M Visa | Business activities like meetings, conferences, trade visits | Varies |
Z Visa | Employment in China | Varies |
X1 Visa | For students who intend to study in China for more than 180 days | >180 days |
X2 Visa | For students who intend to study in China for up to 180 days | ≤180 days |
Q1 Visa | For long-term family reunions with Chinese citizens or permanent residents | >180 days |
Q2 Visa | For short visits to family members who are Chinese citizens or permanent residents | ≤180 days |
S1 Visa | For long-term visits to foreign relatives working or studying in China or other reasons | >180 days |
S2 Visa | For short visits to family members who are foreigners working or studying in China or other reasons | ≤180 days |
J1 Visa | For foreign journalists/resident media staff stationed in China | >180 days |
J2 Visa | For foreign journalists on temporary assignment | ≤180 days |
C Visa | Crew members of airlines, trains, ships | Varies |
F Visa | Exchanges, visits, study tours | Varies |
D Visa | Permanent residency in China | Long-term |
R Visa | High-level talents or whose skills are urgently needed in China | Varies |
G Visa | Transit through China | Varies |
✨Note: According to the latest update, if you're transiting through China, you can enjoy a 24-hour visa-free stay, and in some cases, a 72-hour or 144-hour visa-free stay, depending on your nationality and entry point, all without needing a G visa. If you want to apply for China visa for domestic helper, S2 Visa is required.
China Visa Requirements
For general China Visa
- A valid passport (with at least 6 months of validity and at least 2 blank visa pages).
- A completed visa application form (available on the Chinese embassy's website).
Requirement | Details |
Passport | Two blank pages, one copy of the passport photo data page, and the most current Chinese visa (if granted) are required for a minimum of six months of validity. |
Photo | Recent passport-sized photo with a white background. |
Visa application form | Completed online and printed (via the China Visa Application Service Center). |
Proof of purpose | Documents supporting the type of visa (e.g., business letters, tourist plans, invitation letters). |
Visa fee | Fees vary based on visa type and number of entries. |
Other special documents for various visas
You may need some special documents for differnt kinds of China Visa:
C Visa (Crew Visa)
Letter of guarantee from foreign transportation company or invitation letter from China.
D Visa (Permanent Residence Visa)
"Foreigner Permanent Residence Status Confirmation Form", often called "Certificate of Permanent Residence (CPR)" issued by the Ministry of Public Security of China.
F Visa (Cultural Exchange, Visit, Study Visa)
Verification of Invitation Letter (TE) from the inviting party in China or invitation letter from related entity or individual in China. Additional documents such as support letter, bank account, and police record certificate may be required.
G Visa (Transit Visa)
Original Seaman's Book and photocopy, letter from ship owner company, and Ministry of Maritime Affairs.
J1 and J2 Visa (Journalist Visa)
Visa Notification Letter from Ministry of Foreign Affairs and official letter from journalist organization.
L Visa (Tourist Visa)
Note for Pakistani Citizens: Must join a tourist group arranged through a qualified travel agency.
M Visa (Business Visa)
Verification or Invitation Letter (TE) from the inviting party in China, and other relevant documents such as tax payment certificate and company registration.
Q1 and Q2 Visa (Family Reunion Visa)
Invitation letter from family members in China, proof of family relationship, and other relevant documents.
R Visa (Talent Visa)
Relevant certification according to Chinese government requirements.
S1 and S2 Visa(Private Visit Visa)
Invitation letter from foreign residents in China, proof of relationship, and other relevant documents.
X1 and X2 Visa (Study Visa)
Acceptance Letter and Visa Application for Study in China (form JW201 or JW202), score sheet, and bank statement.
Z Visa (Employment Visa)
Work permit, work permit, or other relevant documents.
China Tourist Visa: Single/Double/Multiple Entry

Source: Wikipedia
When applying for a China tourist visa (L visa), you’ll need to choose the type of entry that suits your travel plans. The visa type determines how many times you can enter China during the visa’s validity.
1. Single Entry Visa
- ✅ Entry: Only once during the visa’s validity.
- ⏳ Validity & Stay: The visa usually has a validity of 3 months to 6 months, and you can stay for a limited period per entry (commonly 30 days).
- 🛬 Usage: Once you leave China, the visa expires, even if the validity period hasn’t ended.
- 💡 Best for: Travellers with a one-time trip who don’t plan to exit and re-enter China.
⚠️ Tip: If your trip involves visiting nearby countries (e.g., Hong Kong, Macau, or Vietnam) and returning to China, a single-entry visa won’t allow you back in—you’ll need a new visa.
2. Double Entry Visa
- ✅ Entry: Allows two entries within the visa’s validity period.
- ⏳ Validity & Stay: Typically valid for 3–6 months, with each stay limited to 30 days.
- 🛬 Usage: Useful if your itinerary involves leaving China briefly and coming back, such as a short trip to Hong Kong or Macau.
- 💡 Example: You fly to Beijing, then take a 3-day trip to Hong Kong, and re-enter Beijing to continue your travel.
⚠️ Tip: Make sure you calculate your stay carefully—overstaying on either entry can lead to fines or trouble with immigration.
3. Multiple Entry Visa
- ✅ Entry: Allows multiple entries during the visa’s validity period, usually 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, 5 years and 10 years.
- ⏳ Validity & Stay: Each entry may allow a stay of 30–60 days, depending on the visa. You can enter China as many times as you like, as long as the visa remains valid.
- 🛬 Usage: Ideal for frequent travellers, business visitors, or people who want to explore different regions in multiple trips.
- 💡 Example: You plan a spring trip to Shanghai, return home, and then visit Guangzhou in autumn—multiple-entry visa covers all these trips without applying again.
⚠️ Tip: Multiple-entry visas are slightly more expensive and may require extra documentation, such as proof of previous travel or accommodation bookings.
Note: You may need to show sufficient funds to cover multiple trips (bank statements, pay slips, or savings proof). Sometimes, the consulate may request a short explanation of why multiple entries are needed, e.g., frequent trips for sightseeing, family visits, or business-related tourism.
How to Apply for a China Visa?

Source: Educational School Trip
👀Before applying for China Visa, make sure you have already confirmed the right visa type and prepared the relevant documents.
1. Apply for your application
Apply for China Visa online: Fill out the China Online Visa Application (COVA) form at the Chinese Visa Application Service Center (CVASC). Select the correct Embassy or Consulate-General based on your location. Upload the visa application documents, including passport, photo and required supporting documents. You can fill out on Chinese Visa Application Service Center website: https://www.visaforchina.cn/SGP3_EN/qianzhengyewu.
Ensure you fill in all the required information accurately. You might receive a confirmation email when the application online has been approved online, and the status will be shown as “Approved”.
2. Submit your application
- Print the completed COVA form and sign it.
- Submit your application and documents to the designated Visa Centre.
Please bring the following documents, and you might be required to provide more documents at the Centre if deemed necessary.
- Visa Application Certificate (attached to the Approval email).
- Original passport.
- A photo if the uploaded one is indicated as unqualified.
- The first and seventh pages of the Application Form, and sign on the seventh page.
- Original certificate of kinship or house ownership, if have been required to be uploaded.
- Printed documents with barcode, if have been required to be uploaded.
- If you apply for a two-year multiple visa, please bring printed application form with all pages and all application documents.
3. Pay the visa fee
Fees vary based on visa type and processing speed (standard, express, or rush). Payment is typically made during submission.
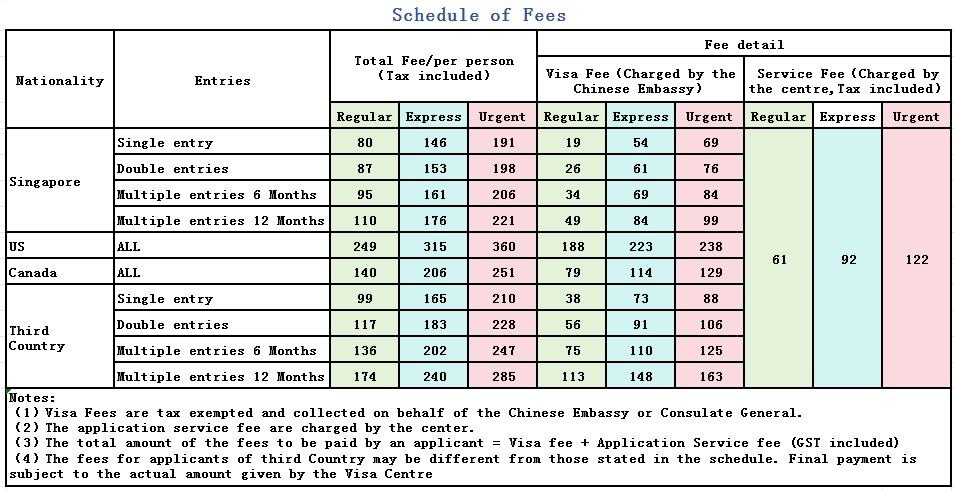
Source: Chinese Visa Appilication Service Center
3. Collect your visa
Processing usually takes 4-5 working days for standard service. You’ll be notified when your visa is ready for collection.
Travel Tips for Entering China

- Payment: Alipay and WeChat Pay are widely used. You can set these up before arrival but keep some cash handy, as not all places accept foreign credit cards.
- Connectivity: Many foreign websites and apps (e.g., Google, Facebook, WhatsApp) are restricted in China. Hence you can download a reliable VPN before arrival. You can buy a local SIM card or a China eSIM for easy access.
- Customs regulations: Declare any prohibited or restricted items (e.g., certain medications, large sums of cash).
- Transportation tips: China high-speed rail is convenient for intercity travel. Book tickets early, especially during holidays. For taxis, you can download DiDi (China’s equivalent of Grab) for ride hailing.


